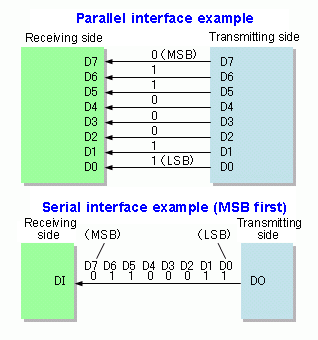
Serial data transmission implies that one bit is sent after another (bit-serial) on a single transmission line. Since the microprocessors in the devices pro-cess data in bit-parallel mode, the transmitter performs parallel-to-serial conversion, while the receiver performs serial-to-parallel conversion (Fig. This is done by special.


Serial Data Transmission
- A. S. Tanenbaum, “Computer Networks”, pp 37-46,184-187.Google Scholar
- D. E. Comer, “Computer Networks and Internets”, pp 94-96, 229-230, 236-237.Google Scholar
- P. C. Gupta, “Data Communications”, pp 152-156, 165-169, 418-434.Google Scholar
- P. Keleher, S. Dwarkadas, A. L. Cox, and W. Zwaenepoel. Treadmarks: Distributed Vern Paxson. Automated packet trace analysis of TCP implementations. In SIGCOMM, pp-167-179, 1997.Google Scholar
- E. Kohler, M. F. Kaashoek, and D. R. Montgomery. A readable TCP in the J. Postel. Transmission control protocol. RFC 793, USC/Information Sciences Institute, September 1981.Google Scholar
Serial And Parallel Data Transmission
PARALLEL VERSUS SERIAL DATA TRANSMISSIONS There are two methods of transmitting digital data. These methods are parallel and serial transmissions. In parallel data transmission, all bits of the binary data are transmitted simultaneously. Parallel Data Transmission: A Proposed Multi-layered Reference Model 1Thomas Chowdhury. Understand either the starting data transmission is serial or parallel transmission. In the case of parallel. A PROPOSED MULTI-LAYERED REFERENCE MODEL 141. GCSE Computer Science/Serial and parallel data transmission. From Wikibooks, open books for an open world. Show understanding of the reasons for choosing serial or parallel data transmission - 2016 CIE Syllabus p11. Show understanding of the use of serial and parallel data transmission, in Universal Serial Bus (USB) and Integrated.



